What to know about Antibiotics:Antibiotics work by killing bacteria and preventing them from multiplying Common antibiotics include gentamicin cephalexin ertapenem erythromycin ciprofloxacin and metronidazole

They include a range of powerful drugs used to treat diseases caused by bacteria Antibiotics cannot treat viral infections such as cold flu and most coughs.What to know about Antibiotics
This article explains what antibiotics are how they work potential side effects and antibiotic resistance
Fast facts on antibiotics

- Alexander Fleming discovered penicillin the first natural antibiotic in 1928
- Antibiotics cannot fight viral infections.
- Fleming predicted the rise of antibiotic resistance
- Antibiotics either kill or slow the growth of bacteria
- Side effects can include diarrhea an upset stomach and nausea
What are Antibiotics

Antibiotics are powerful medications that treat certain infections and save lives when used properly They either stop bacteria from reproducing or destroy them.

Before bacteria can multiply and cause symptoms the immune system can typically kill them White blood cells WBCs attack harmful bacteria even if symptoms occur the immune system can usually cope and fend off the infection.
However sometimes the number of harmful bacteria is excessive and the immune system cannot clear them all Antibiotics are useful in this scenario.
The first antibiotic was penicillin penicillin based antibiotics such as ampicillin amoxicillin and penicillin G are still available to treat a variety of infections and have been in use for many years.
Several types of modern antibiotics are available and they are usually only available with a prescription in the United States Topical antibiotics are available in over the counter OTC creams and ointments.
How do antibiotics work?
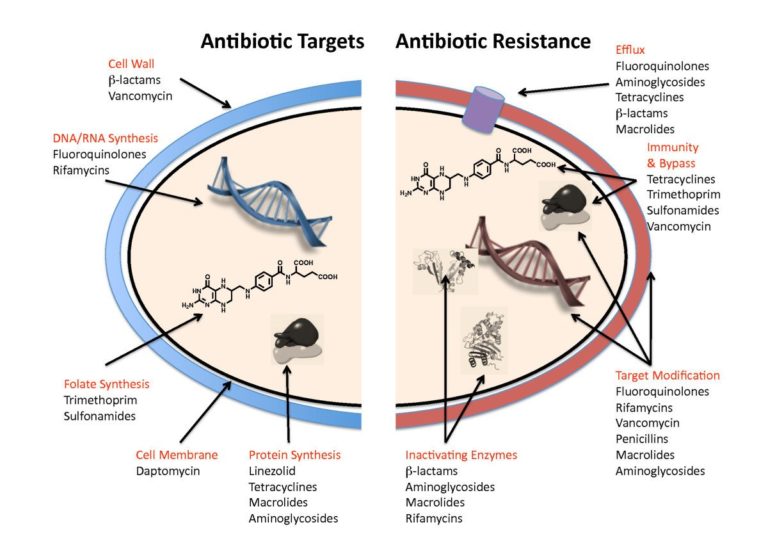

There are different of antibiotics which work in their unique way However the two main they work include:
A bactericidal antibiotic such as penicillin kills the bacteria these drugs usually interfere with either the formation of the bacterial cell wall or its cell contents.
A bacteriostatic stops bacteria from multiplying it may take a few hours or days after taking the first dose before people feel better or their symptoms improve.
Types of antibiotics

There are various classes or groups of antibiotics which depend on their chemical structure Some classes of antibiotics include the following.
- Amoxicillin ( Amoxil)
- Azithromycin ( Zithromax) and erythromycin
- Ciprofloxacin ( Cipro) and levofloxacin
- Amoxicillin /clavulanate
- clindamycin ( clindex )
- Sulfamethoxazole ( Bactrim Septra Sulfatrim
- cephalexin ( Keflex and cefdinir
This list is not inclusive other classes and brand names exist in addition penicillin cephalosporins and other antibiotics may be regarded as subclasses of beta lactam drugs
Why is it important to take antibiotics when needed
Experts advise using antibiotic only when they are needed This is to ensure that the bacteria is killed and is unable to multiply and spread to other parts of the body.

Also antibiotic use can sometimes be associated with side effects and antibiotic resistance.
Resistance
Antib iotic resistance occurs when germs no longer respond to the antibiotic designed to kill them inappropriate prescription of antibiotic is driving up the incidence of antibiotic resistance.
iotic resistance occurs when germs no longer respond to the antibiotic designed to kill them inappropriate prescription of antibiotic is driving up the incidence of antibiotic resistance.
Sometimes prescription of the wrong medication or the wrong dosage can lead to antibiotic misuse Misuse can also occur when people do not take antibiotics as their doctor prescribes Some measures people can take include finishing the treatment course and not sharing antibiotic medications with other even if they have the same symptoms.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention ( CDC) state that in the united States around 47 million antibiotic courses are inappropriately prescribed to people meaning their illness did not require antibiotics.

Some bacteria such as Enterobacterales can become resistant to carbapenems a major class of last line antibiotic Enterobacterales are an order of bacteria that can cause pneumonia meningitis and other diseases Escherichia coli
CRE or carbapenem resistant Enterobacterales pose a major concern to people in hospitals and other healthcare settings
Experts believe that carbapenem resistance may lead to
- a greater incidence of disease
- a reduction in the effectiveness of initial antibiotic therapy
- poorer outcomes
Is it bad to take antibiotics a few times a year
A person should only take antibiotic when they need them and when their doctor prescribes them if person needs to take antibiotics regularly their doctor may look at other treatment options or take steps to identify what is causing frequent infections.What to know about Antibiotics